| Recent Comments |
| Categories |
| Archives |
| Tags |
Why you don’t need Thunderbolt for professional audio (by RMA Audio) (Monday 10 April, 2023)
Audio isn’t a very demanding nor resource-intensive data stream. To transmit a 24bit 44.1kHz audio file you need a bandwidth of 2116 kbit/s (2Mbits/s), which is a tiny fraction of the full USB 2.0 bandwidth (480 MBit/s). In general, we need a bandwidth of Sample rate x Bit Depth x Number of Changes. In theory, USB2.0 would give us 240 stereo channels of 24 bit / 44.1 kHz (leaving out control data and other non-audio data). See video for further details.
Only a small fraction of the USB 2.0 bandwidth is required to transmit a 24 bit / 44.1 kHz audio file.
Even the transmission of steroe 24 bit 192 kHz audio file requires still a fraction of the USB 2.0 bandwidth.
Background
Thunderbolt is the brand name of a hardware interface for the connection of external peripherals to a computer. It can transmit data with a speed of 10 – 40 Gbit/s (much faster than USB 2.0). It has been developed by Intel, in collaboration with Apple. Thunderbolt combines PCI Express (PCIe) and DisplayPort (DP) into two serial signals and additionally provides DC power, all in one cable. PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers’ graphics cards, sound cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. DisplayPort (DP) is a digital display interface developed by a consortium of PC and chip manufacturers and standardized by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). It is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor. It can also carry audio, USB, and other forms of data. Up to six peripherals may be supported by one connector through various topologies. Thunderbolt 1 and 2 use the same connector as Mini DisplayPort (MDP), whereas Thunderbolt 3 and 4 reuse the USB-C connector from USB.
- Apple MacBook Pro, model A1278
Thunderbolt 1/2 and Thunderbolt 3/4 connectors
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables, connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply between computers, peripherals and other computers. USB 2.0 was released in April 2000, adding a higher maximum signaling rate of 480 Mbit/s. The USB 3.0 specification was released on 12 November 2008. USB 3.0 adds a SuperSpeed transfer mode. The SuperSpeed bus provides for a transfer mode at a nominal rate of 5.0 Gbit/s. USB 3.2, released in September 2017, preserves existing USB 3.1 SuperSpeed and SuperSpeed+ data modes but introduces two new SuperSpeed+ transfer modes over the new USB-C connector with data rates of 10 and 20 Gbit/s. USB-C (properly known as USB Type-C; commonly known as just Type-C) is a 24-pin USB connector system with a rotationally symmetrical connector. The designation C refers only to the connector’s physical configuration or form factor and should not be confused with the connector’s specific capabilities, which are designated by its transfer specifications (such as USB 3.2).
- MSI Bravo 17 laptop USB-C port
USB 2/3 and USB-C connectors.
USB speeds and connectors (copied from Wikipedia)
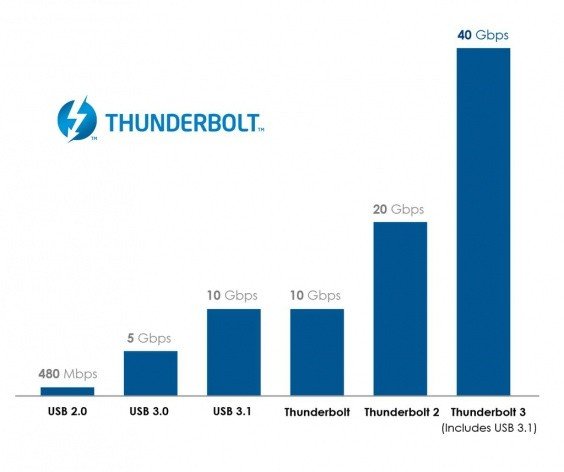
Thunderbolt speeds in relation to USB.
How many USBs can you plugin at once?
To monitor your USB ports use USB Device Tree Viewer.